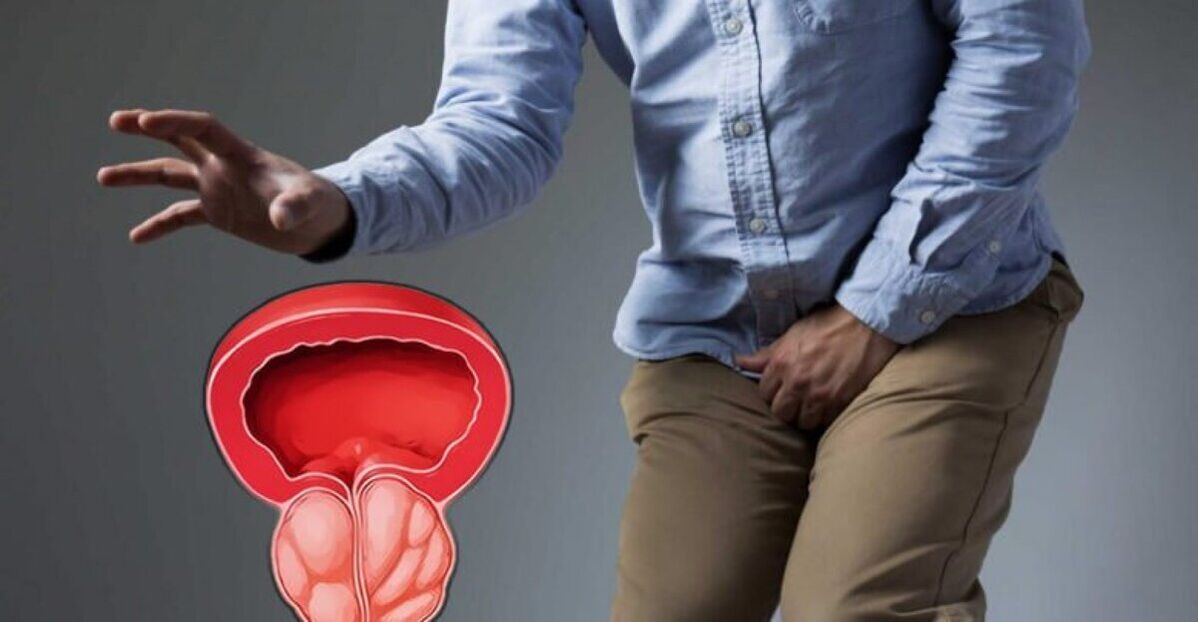
Definition of disease. disease cause
- Bacterial infection: This is the most common cause of prostatitis. Bacteria can enter the prostate through the genitourinary tract or bloodstream and cause inflammation.
- Chronic constipation: Chronic constipation can put pressure on the prostate, leading to inflammation.
- Sexual problems: Long-term lack of sexual activity or sexual fatigue can lead to the occurrence of prostatitis.
- Autoimmune diseases: Some autoimmune diseases can cause inflammation of the prostate.
- Prostate damage: Prostate damage can lead to inflammation.
- Irregular sexual life: Lack of regular sexual activity can cause stagnation of prostate secretions, causing inflammation.
symptoms of prostatitis
- Pain and discomfort in the perineum, rectum, or bladder.
- Painful urination, sometimes with burning or pain.
- Need to urinate more often than usual, including at night.
- Urine flow is weak, intermittent, or difficult.
- Sexual problems, such as pain or discomfort during erection or ejaculation.
- Feeling tired or generally weak.
- Increased body temperature and fever.
- Increased sensitivity to cold.
- Pain when pressure is placed on the prostate.
- The presence of blood in the urine or semen.
The pathogenesis of prostatitis
Classification and development stages of prostatitis
- Bacterial prostatitis is caused by a bacterial infection.
- Chronic prostatitis/chronic post-prostatitis syndrome is characterized by persistent symptoms without detectable inflammatory processes.
- Chronic nonbacterial prostatitis due to noninfectious causes.
- Acute prostatitis is characterized by rapid onset, severe pain, and severe symptoms.
- Acute prostatitis. The onset is rapid and the symptoms are severe, such as pain, burning sensation during urination, and fever. Acute prostatitis may be caused by a bacterial infection and requires immediate treatment.
- Chronic prostatitis/chronic post-prostatitis syndrome. Symptoms persist and can last for months or even years. There may be no inflammatory process, and symptoms may be non-infectious in nature.
- Chronic nonbacterial prostatitis. Symptoms persist, but no inflammatory process is detected. This type of prostatitis can be caused by a variety of reasons, such as stress, long-term constipation, microcirculation disorders, etc.
Complications of prostatitis
- Prostate cancer.
- Epididymitis is inflammation of the testicles.
- Sclerosing lymphangitis.
- Seminal vesicle cyst.
- septicemia.
- Prostate dysfunction.
- Increased risk of depression and other psychological problems.
Diagnosis of prostatitis
Treatment of prostatitis
forecast. prevention
- Maintaining hygiene means washing your genitals regularly and using condoms during sex.
- Avoid hypothermia - Clothing should be appropriate for the weather conditions and sitting on cold surfaces should be avoided.
- Quit smoking and drinking.
- Eat right and drink enough water.
- Regular physical exams to detect genitourinary diseases.
- Regular exercise and stress management.